Introduction:
Compared with usual care, Collaborative Care has been shown to improve the effectiveness of depression treatment and lower total healthcare costs. This handout outlines those differences using data from the IMPACT trial.
A printable PDF is available for download; however, please note that this document may not conform to the WCAG-2 accessibility standards.
Comparing Collaborative Care to Usual Care
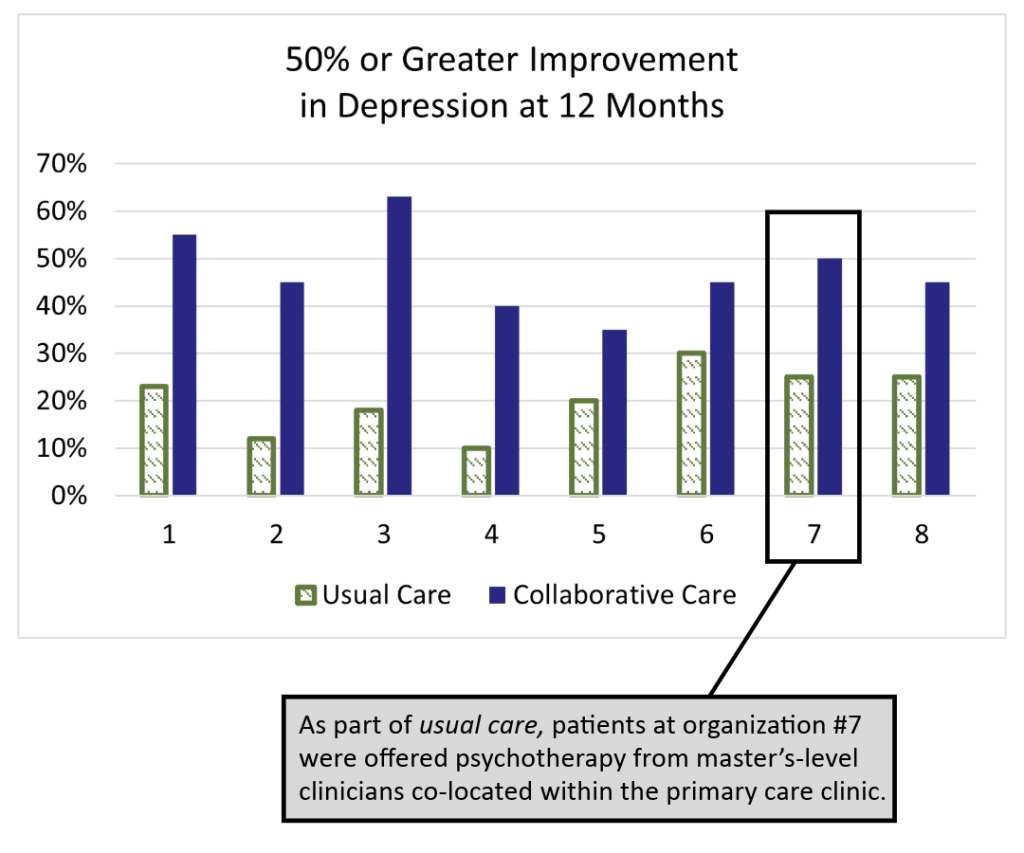
The IMPACT (Improving Mood: Providing Access to Collaborative Treatment) trial focused on depressed, older adults. Half were randomly assigned to receive the depression treatment usually offered by participating clinics, and half were randomly assigned to receive collaborative care. Collaborative care more than doubled the effectiveness of depression treatment and reduced total healthcare costs at the same time (JAMA, 2002).
Usual Care
50% of study patients used antidepressants at the time of enrollment, but were still significantly depressed.
70% of usual care patients received medication therapy from their PCP and/or a referral to specialty behavioral health.
Only 20% of patients showed significant improvements after one year, which matches national data for depression treatment in primary care.
Collaborative Care
On average, twice as many patients significantly improved. The difference was statistically significant in all eight healthcare settings. Why?
- Patient-Centered Team Care
- Population-Based Care
- Measurement-Based Treatment to Target
- Evidence-Based Care
- Accountable Care