The Brief Pain Inventory is a medical questionnaire used to measure pain, developed by the Pain Research Group of the WHO Collaborating Centre for Symptom Evaluation in Cancer Care.
Audience: Primary Care Provider
PHQ-9 Depression Scale Questionnaire
The PHQ-9 is a measurement tool providers can use to ensure measurement-based treatment to target within Collaborative Care. This concise nine-item health questionnaire can function as a screening tool, aids in diagnosis, and measures treatment response.
Advantages of the PHQ-9

- It is shorter than other depression rating scales
- Multiple administration options (in person by a clinician, by telephone, or self-administered by the patient)
- Facilitates diagnosis of major depression
- Assesses symptom severity
- Well-validated and documented in a variety of populations
- Directly based on the nine diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder in the DSM-5
- Valid for use in adolescents as young as 12 years of age
How to Use the PHQ-9
At the initial visit, the PHQ-9 aids in the diagnosis and identification of potential depressive symptoms. At follow-up visits, it measures treatment response. The Questionnaire can be clinician or self-administered.
Scoring the PHQ-9
The PHQ-9 is a tool to assist clinicians in identifying and diagnosing major depression. It has a maximum score of 27. Elevated scores strongly correlate with a major depression diagnosis. However, it’s essential to remember that not everyone with a high PHQ-9 score will have major depression. Trained clinicians must make the final diagnosis.
Patient Health Questionnaire 2 (PHQ-2)
The Patient Health Questionnaire 2 (PHQ-2) effectively screens large groups for depression. It consists of the first two questions on the PHQ-9. If the patient responds affirmatively to either question on the PHQ-2, the PHQ-9 should be administered. No permission is required to reproduce, translate, display, or distribute the PHQ-2.
PHQ-9 Questionnaire and Translations
The PHQ-9, translations of the measure, and an instruction manual are available at www.phqscreeners.com. No permission is required to reproduce, translate, display, or distribute the PHQ-9.
Protocols for Suicide Prevention
The PHQ-9 asks about suicidal ideation, and clinics should have a plan in place for when a patient scores positive on this question. The Protocols for Suicide Prevention in Primary Care assists clinics in refining existing protocol(s) for responding to patients who present with suicidality or violent behavior.
PHQ-9 Aids
Introducing the PHQ-9
To increase staff comfort in discussing the PHQ-9 with patients, the AIMS Center provides the Helping Clinic Staff Talk about the PHQ-9 tool. This resource equips clinic staff to administer the PHQ-9 by addressing commonly asked patient questions.
PHQ-9 Visual Answer Aid
This answer aid visually represents the PHQ-9 answer scale: English | Spanish.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder subscale (GAD-7)
The Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) subscale of the Patient Health Questionnaire (GAD-7) is a quick and easy tool to help identify patients with anxiety and monitor treatment response. The GAD-7 is available free for clinical use in a variety of languages at the link below.
AUDIT-C
The AUDIT-C is a 3-item alcohol screen that can help identify persons who are hazardous drinkers or have active alcohol use disorders (including alcohol dependence). The AUDIT-C is a modified version of the 10-question AUDIT instrument.
Why Practice Collaborative Care?
Introduction:
This resource outlines the benefits of Collaborative Care and is designed to be shared with PCPs, stakeholders, and others looking to implement CoCM.
For a printable version, download the resource below. A printable PDF is available for download; however, please note that this document may not conform to the WCAG-2 accessibility standards.
Why Practice Collaborative Care?
Collaborative care (CoCM) is beneficial to primary care providers (PCPs) and their patients because it offers better
medical care, access to psychiatry experts, helps with challenging patient cases, and team collaboration.

Established Evidence Base
- CoCM has a robust evidence base of over 80 randomized controlled trials and has been shown to be the best approach to treating depression in many populations and settings.
- CoCM has a strong and expanding evidence base for its use with diverse behavioral health diagnoses such as anxiety, posttraumatic stress disorder, chronic pain, and dementia.

Better Medical Outcomes
- CoCM is linked to better medical outcomes for patients with diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and chronic arthritis.
- CoCM is recommended as a primary prevention strategy for cardiovascular events in patients without preexisting heart disease (Psychosomatic Medicine, 2014).

Help with Challenging Patient Cases
- Many challenging cases likely have patients with untreated or undertreated behavioral health conditions. Behavioral health providers do the follow-up and intervention tasks that a busy PCP doesn’t have time to do, but make a big difference for patients.
- PCPs are generally more satisfied working within an integrated behavioral health care program than within usual care (Family Community Health, 2015).

Faster Improvement
- A 2016 retrospective study at Mayo Clinic found that the time to depression remission was 86 days in a CoCM program while in usual care it was 614 days.
- Analysis of a large CoCM implementation found that early, intense intervention by the behavioral health provider was key to early improvement in patients with depression symptoms (Psychiatric Services, 2015).
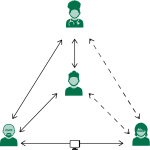
It Takes a Team
- CoCM uses an enhanced care team to provide a population based, treat-to-target approach to care. Through shared care planning, the team makes proactive changes in treatment to make sure that no patients fall through the cracks.
- Only 30-50% of patients have a full response to the first treatment. That means 50-70% of patients need at least one treatment adjustment. Additional experts can help.
Comparing Collaborative Care to Usual Care
Introduction:
Compared with usual care, Collaborative Care has been shown to improve the effectiveness of depression treatment and lower total healthcare costs. This handout outlines those differences using data from the IMPACT trial.
A printable PDF is available for download; however, please note that this document may not conform to the WCAG-2 accessibility standards.
Comparing Collaborative Care to Usual Care
The IMPACT (Improving Mood: Providing Access to Collaborative Treatment) trial focused on depressed, older adults. Half were randomly assigned to receive the depression treatment usually offered by participating clinics, and half were randomly assigned to receive collaborative care. Collaborative care more than doubled the effectiveness of depression treatment and reduced total healthcare costs at the same time (JAMA, 2002).
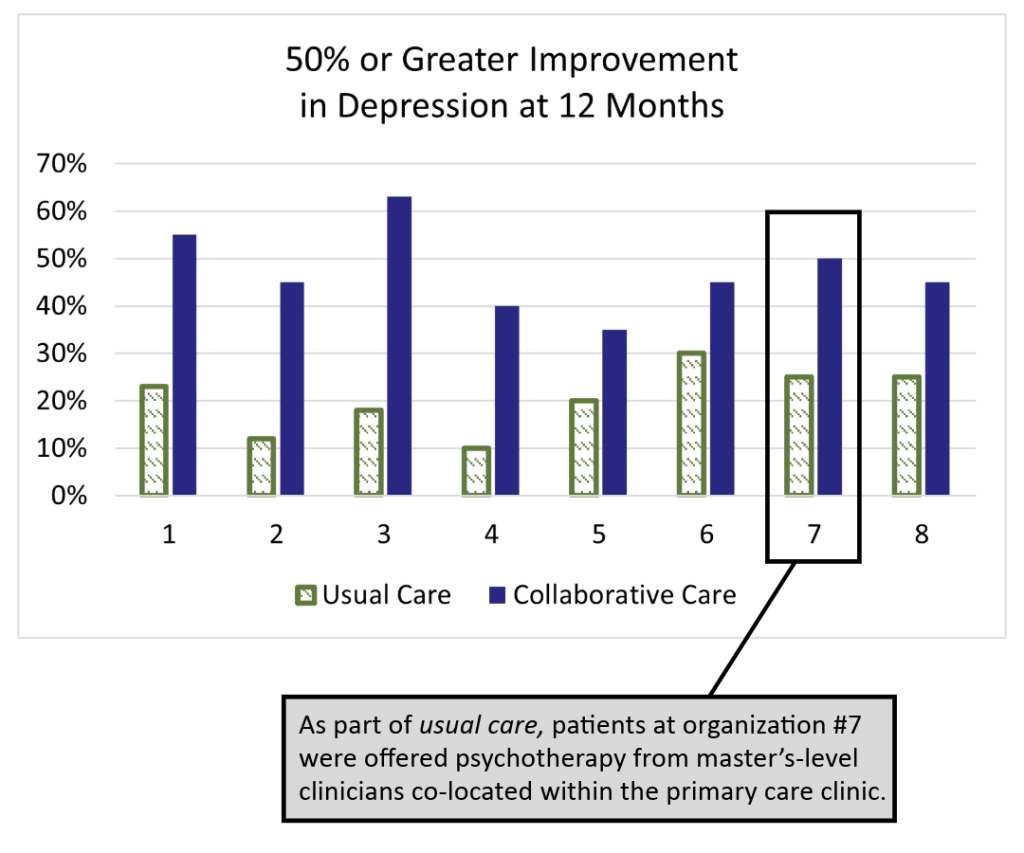
Usual Care
50% of study patients used antidepressants at the time of enrollment, but were still significantly depressed.
70% of usual care patients received medication therapy from their PCP and/or a referral to specialty behavioral health.
Only 20% of patients showed significant improvements after one year, which matches national data for depression treatment in primary care.
Collaborative Care
On average, twice as many patients significantly improved. The difference was statistically significant in all eight healthcare settings. Why?
- Patient-Centered Team Care
- Population-Based Care
- Measurement-Based Treatment to Target
- Evidence-Based Care
- Accountable Care
Tips for Discussing Trauma During an Initial Assessment
Introduction
Trauma can increase the risk of health, social, and emotional problems. Despite the high prevalence of patients with a past history of trauma, few clinics or Collaborative Care teams have a protocol for addressing it. These three tips can help clinicians safely and effectively discuss the trauma history of their patients during their initial assessment.
A printable PDF is available for download; however, please note that this document may not conform to the WCAG-2 accessibility standards.
Discussing Past Trauma with Patients During an Initial Assessment
Many patients with depression have experienced trauma in their lives. Discussing the past traumas in a patient’s life can be tricky due to the risk of re-traumatization or re-triggering the symptoms related to Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). It is also common for the patient to dissociate as a defense mechanism to avoid their past trauma. We have compiled a few tips to help clinicians talk with their patients about past trauma and safely learn their stories during an Initial Assessment.
This is only the beginning of a very complex subject. For more information about caring for patients with trauma history, please read “TIP 57: Trauma-Informed Care in Behavioral Health Services” by SAMHSA.
Tip 1
To prevent re-traumatizing or re-triggering PTSD symptoms, encourage the patient to respond with short, concise descriptions of the trauma.
- Ask for a 2-3 sentence or <25 word description to get a general sense of the trauma.
- Be directive and feel free to stop the discussion if you see the patient is having trouble containing their emotions.
- Normalize the extreme difficulty patients often have when re-telling their stories.
Tip 2
Don’t start with a checklist! Patients often have post-injury concerns and interpret trauma uniquely.
- Encourage the patient to tell their story in their own words.
- Ask open-ended questions.
- Remember, you don’t need all the details to make the diagnosis or treat depression!
Tip 3
If you notice the patient dissociate, work with them to help them get grounded and then educate them on dissociation.
- A way to help ground the patient is to direct them to engage in their immediate environment.
- Once they are grounded, educate them on dissociation.
Tips adapted from: Stephens, K., & Bentham, W. (2010, June 17). PTSD in Primary Care. Mental Health Integration Program (MHIP) Webinar.
Primary Care Provider Role Handout
Introduction
Primary care providers (PCP) identify and engage patients in collaborative care, make diagnoses, and treat patients. The resource below describes the role of the PCP in more detail.
A printable PDF is available for download; however, please note that this document may not conform to the WCAG-2 accessibility standards.
The Role of the Primary Care Provider in Collaborative Care
The role of the primary care provider (PCP) in Collaborative Care (CoCM) is to oversee all aspects of a patient’s behavioral health care, including encouraging the patient’s participation, prescribing medications, and making referrals to specialty mental health care when needed. PCPs work in close collaboration with the patient’s behavioral health care manager (BHCM) and psychiatric consultant. This is summarized below.
Collaborative Care Team
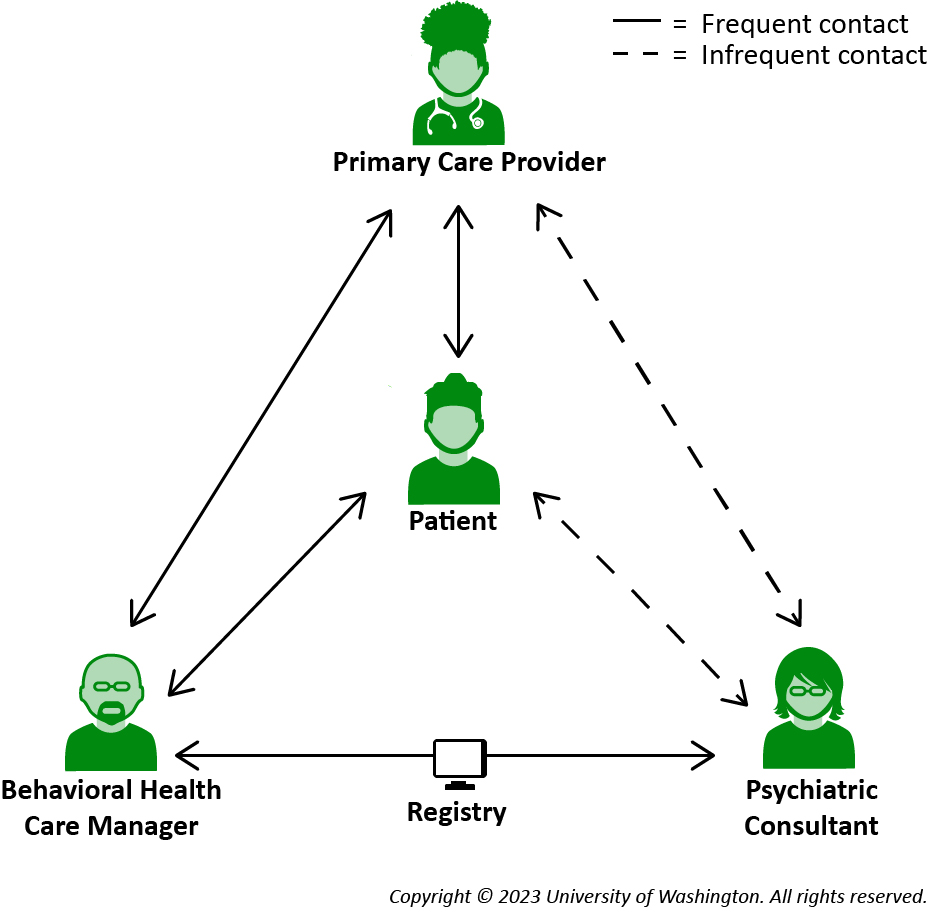
Identifies and Engages
- Introduces Collaborative Care to a patient
- Acquires informed patient consent
- Initiates a warm connection to a BHCM
Makes Diagnosis
- Formulates using validated screeners, exams, and history
- Works with care team to diagnose complex behavioral health conditions
- Observes over time and adjusts diagnosis as appropriate
Treats
- Works with care team and patient to develop a treatment plan
- Works with care team to implement treatment and make treatment adjustments
- Prescribes medications as needed
- Addresses safety concerns
- Monitors physical health and potential medication interactions
Primary Care Provider Champion Role Description
The Primary Care Provider (PCP) Champion plays a key role on the Clinic Implementation Team (CIT). The CIT is created when a medical practice is planning to implement Collaborative Care. This document outlines the PCP Champion’s key responsibilities with the team and their PCP colleagues, as well as the personal and professional characteristics that are most desirable in the role.
PMQ-9 (Spanish)
The Spanish version of the Patient Mania Questionnaire (PMQ-9) is a nine-item scale used to assess and monitor manic symptoms. The PMQ-9 Mania Questionnaire complements use of the PHQ-9 for depressive symptoms to inform measurement-based care. It is also suited for use in mental health care settings. An English version of the PMQ-9 can be found here.